Systems in your body
Chapter 4 endnote 2, from How Emotions are Made: The Secret Life of the Brain by Lisa Feldman Barrett.
Some context is:
Interoception is your brain’s representation of all sensations from your internal organs and tissues, the hormones in your blood, and your immune system.
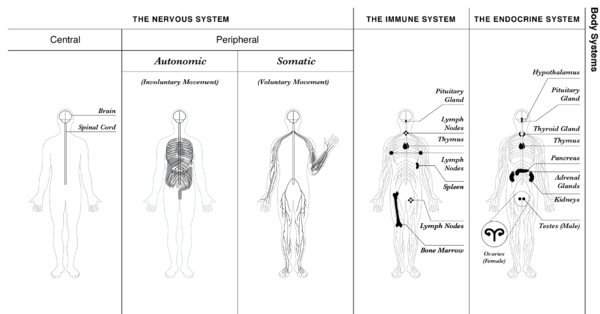
Your body is a confusing array of “systems.” The body contains:
- An autonomic nervous system (the main neural control of your internal organ systems)
- An endocrine system (that circulates hormones through the blood to control metabolism, growth, reproduction)
- An immune system (that protects your body from invaders and injury, also through the blood and other tissues)
Cross cutting this, your body contains various systems of internal organs, such as:
- The digestive system (stomach and intestines)
- The cardiovascular system (heart, blood vessels)
- The respiratory system (lungs)
Even your skin is an organ (important for water and electrolyte balance, and vitamin D production). Your brain also regulates your body’s temperature (called thermoregulation), pain sensation (called nociception), your release of insulin and use of glucose, your salt balance, as well as the concentration of various chemicals in your blood. It has receptors in your muscles to monitor your energy use.
These are just a few examples of "systems" in your body.